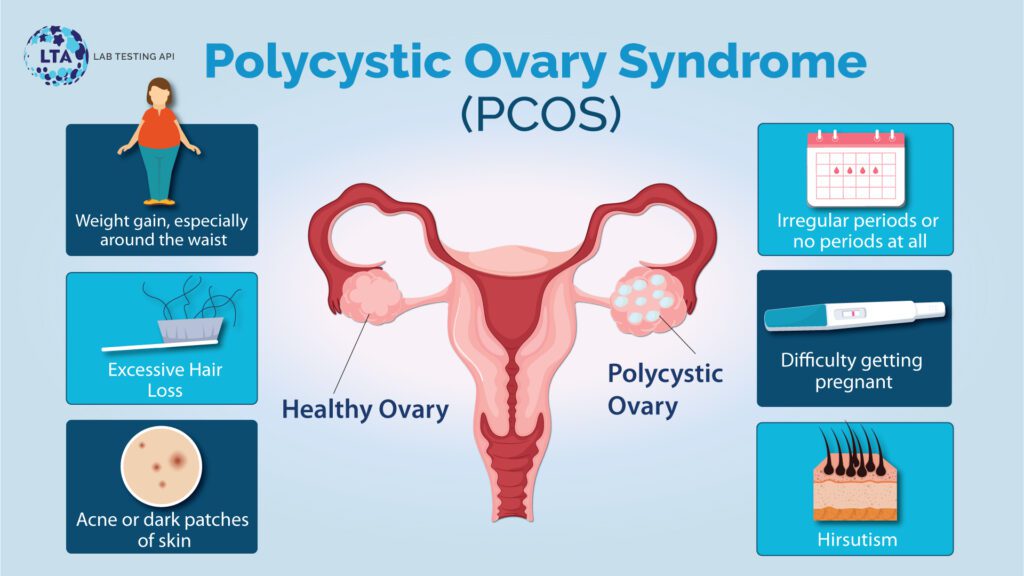
Hormone Testing
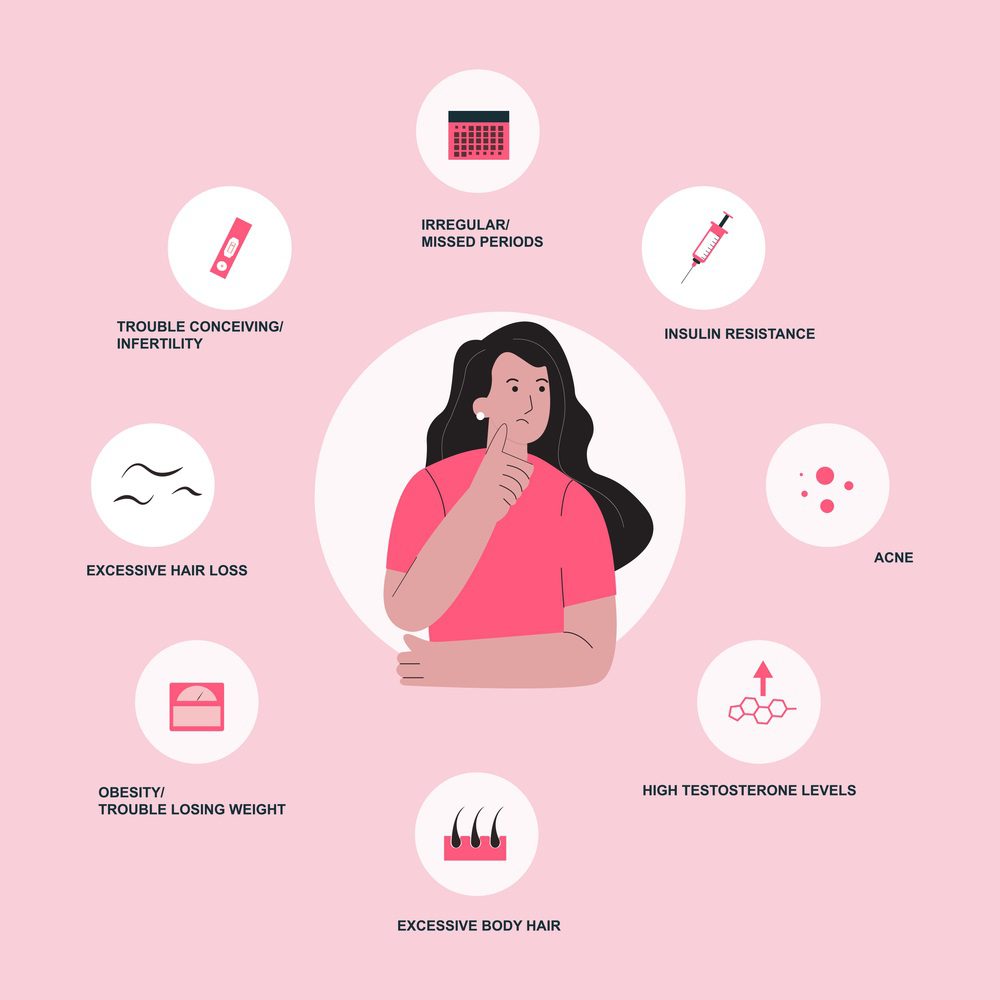
Total and free testosterone are androgenic hormones generated by women’s ovaries and adrenal glands. A growth in free testosterone levels may occur with normal total testosterone levels. As its value rises, masculine characteristics emerge (thick body hair, masculine baldness), which may also be caused by PCOS.
- Prolactin: The hormone prolactin aids in initiating and maintaining milk secretion after childbirth.
- Oestradiol: It is an estrogen hormone that is produced by the developing follicle. The measurement of oestradiol levels is primarily used to evaluate ovarian function.
- Androstenedione: This is an androgenic hormone generated by women’s ovaries and adrenal cortex. Its concentration changes throughout the menstrual cycle, aiding in monitoring ovarian function.
- DHEA-S: an androgenic hormone that can be transformed into a female sex hormone, estrogen, in women.
- Progesterone: It is vital in the creation and maintenance of pregnancy, but it is also involved in regulating the female menstrual cycle.
- AMH (anti-Müllerian hormone): This is produced by eggs still maturing, and its level predicts the length of the fertile phase. Its concentration progressively declines over time.
- FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone, follicle maturation hormone): FSH causes follicles in the ovaries to grow and develop.
- LH (luteinizing hormone, corpus luteum stimulating hormone): LH is the hormone that causes ovulation (follicular rupture). It allows the follicle produced by FSH to grow further; when LH levels rise, ovulation occurs.