The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped small gland in the middle of the lower neck. The foremost function of the thyroid is to control the metabolism of the body. This means the thyroid manages the rate at which the body cells perform duties that are needed for living. In order to control metabolism, it produces T3 and T4 hormones which inform the body cells about how much energy should be utilized. Thyroid dysfunction or Thyroid disorders could either be harmless goiter (enlarged thyroid) which requires no treatment or life-risking cancer. The most common thyroid disorders include unusual production of thyroid hormones such as:
- HYPERTHYROIDISM: This condition involves too much production of thyroid hormone.
- HYPOTHYROIDISM: This condition involves less or insufficient production of thyroid hormone.
What Are The Most Common Thyroid Dysfunctions?
HYPERTHYROIDISM
In hyperthyroidism, the thyroid produces excess thyroid hormones. The thyroid is overactive, therefore, symptoms of hyperthyroidism are mostly related to an increase in the body’s metabolism. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism are:
- Nervousness
- Fatigue
- Sleep disturbance
- Tremors/Muscle weakness
- Increased sweating
- Weight loss
- Increased heart rate
- Heat sensitivity
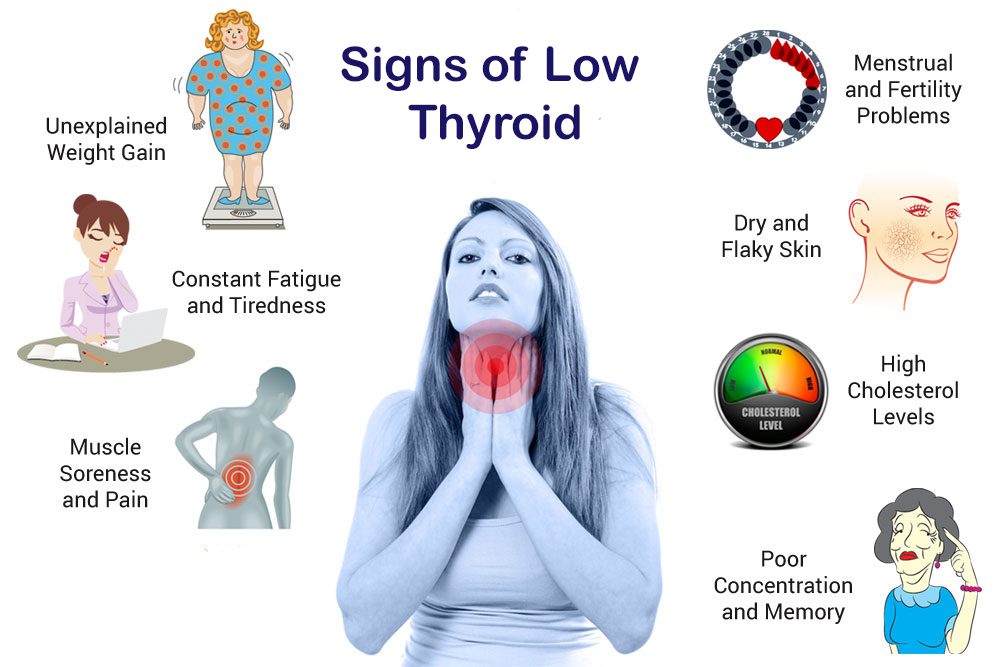
HYPOTHYROIDISM
The thyroid is underactive in hypothyroidism and is unable to produce enough thyroid hormones. Hypothyroidism can develop as a result of problems in the thyroid gland, hypothalamus or pituitary gland. Signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism are:
- Fatigue
- Dry skin
- Constipation
- Cold intolerance
- Depression
- Weight gain
- Heavy menstrual periods
ASSOCIATION OF THYROID DISORDERS WITH LIPID PROFILE
Cholesterol and lipoprotein metabolism is regulated by the thyroid hormones, but, thyroid dysfunction considerably changes lipid profile and gives rise to cardiovascular disease. Therefore, thyroid dysfunction should be considered and taken note of when assessing and treating patients with dyslipidemia.
How Are Thyroid Disorders Diagnosed?
Since symptoms of thyroid dysfunction can easily be confused with other diseases, it can be difficult to detect thyroid disorder. Blood tests can detect the thyroid hormone level; Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Test measures the thyroid hormones and can detect thyroid disorder even before the beginning of the symptoms of the disease.
What Is The Treatment For Thyroid Disorder?
For any thyroid dysfunction, the aim of the treatment is to replace and restore the normal level of thyroid hormones. The most common treatment for thyroid dysfunction is radioactive iodine in which a small dose of an iodine isotope that emits radiation (I-131) is swallowed, the bloodstream and the thyroid gland absorb it, and so, the excess gland cells begin to destroy. in the case of low gland cells, synthetic tablets are taken as a pill. Hypothyroidism (insufficient production of thyroid hormones) can be treated by the drug levothyroxine. This synthetic hormone medication restores missing thyroid hormones in the body. The treatment for Hyperthyroidism (excess production of thyroid hormones) is usually difficult and requires the restoration of normal thyroid hormone levels. The treatment for hyperthyroidism is to normalize the production of thyroid hormone. Hyperthyroidism can be treated through drug therapy that blocks the production of the hormone, radioactive iodine treatment, or, thyroid surgery in which the whole gland is removed,



3 Comments